Uterine Fibroids
Fibroid embolization is the most modern and safest treatment procedure for benign uterine fibroid muscle tumors. Without surgery or hormone drugs, it is highly reliable, top technology and very well accepted and tolerated by most patients. CONTACT US NOW for more information about this procedure at Clinics of the Heart.
Fibroids are muscle tumors growing in the uterus, and they are benign. In other words, they are not associated with cancer. These occur in one of every three women. Uterine fibroids can produce symptoms like:
- Pain
- Longer or more intense menstrual bleeding or uterine hemorrhage
- Difficulties becoming pregnant
- Complicated pregnancies
- Abdomen growing
- Urinary symptoms
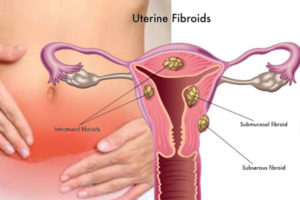
Figure from http://tinylifeboat.com
How are uterine fibroids diagnosed?
A relatively simple and easy diagnosis can be made by conducting an interview and performing some image scans with ultrasound, CT or MRI.
What is the usual approach for treating uterine fibroids?
Surgery is the most common treatment for this disease. This surgery removes only the tumors but, in many cases, it is impossible to do so without removing the entire uterus. The efficiency of this procedure in removing the tumors is good in skilled hands but, even in good hands, complications are sometimes unavoidable. These include hemorrhages, infections, adhesions and scars, all of which can result in a long recovery with the inability to engage in normal activities.
Another treatment approach is possible with hormone drugs, but this approach can’t be long term and, most of the time, it is done simply to prepare the patient for surgery. This treatment may cause other symptoms and complications such as osteoporosis.
Uterine fibroid embolization
Fibroid embolization is the most modern treatment approach for uterine fibroids. This procedure blocks the blood flow to the fibroid tumor making it impossible for oxygen and glucose, both of which are necessary for the persistence of the fibroid, impossible. Embolization is done by inserting, via x-ray in a cath lab, a very thin tube (1.5mm diameter) into the uterine arteries. A material made of very small particles is injected into the arteries, trapping the fibroid. These particles can’t reach other tissues, which is why this approach is the safest of all.
Embolization is minimally invasive and avoids surgery, wounds or scars. It has the highest success rate of all options, especially in interrupting the excessive bleeding so common in this disease. In fact, in most of the women treated by fibroid embolization, the next menstruation is normal.